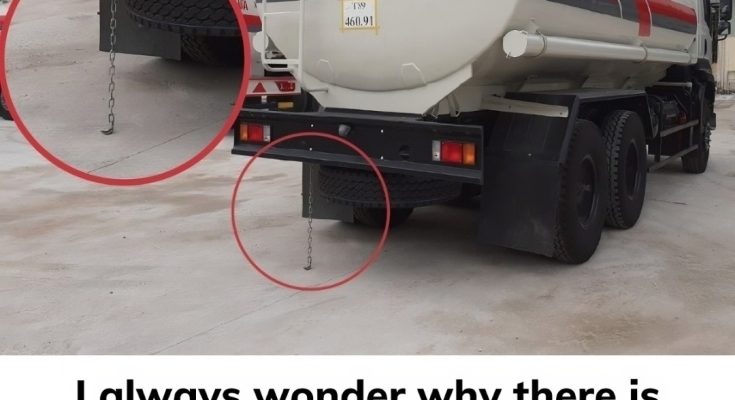
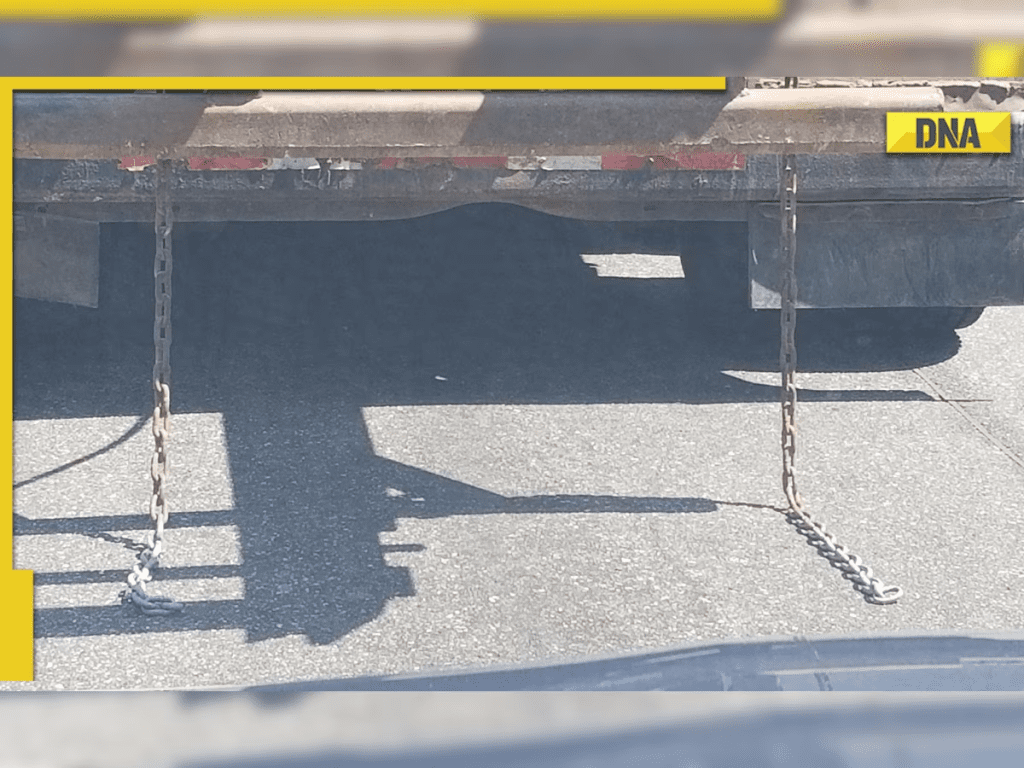
If you’ve ever driven behind a tanker truck carrying gasoline, oil, or other flammable liquids, you might have noticed a metal chain hanging at the back, dragging along the road. While it might seem like an insignificant detail, this extra chain serves a critical purpose in ensuring safety. In this article, we’ll explore why this chain is essential, how it works, and the science behind its role in preventing fires and explosions.
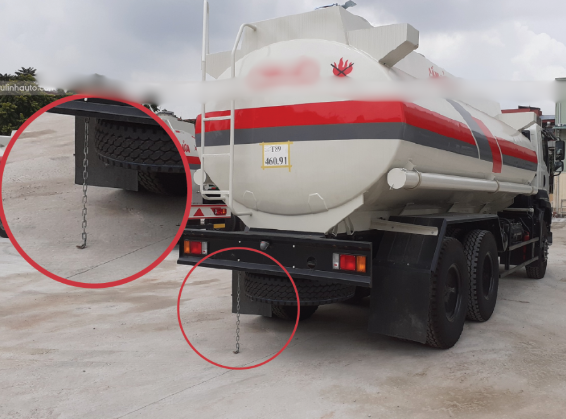

Understanding Static Electricity in Tanker Trucks
To understand the importance of the chain, we first need to talk about static electricity. When a tanker truck moves, especially when carrying flammable liquids like gasoline or oil, static electricity can build up on the tank. This buildup is due to the interaction between the liquid and the dry air inside the tank, as well as friction between the liquid and the tank walls.
When there’s an imbalance of electric charges on the surface of a material, it leads to static electricity. These charges can remain on the surface until they are discharged, which often happens suddenly and creates a spark. In everyday life, you might experience this phenomenon when you touch a doorknob after walking on carpeted floors. While these small sparks are usually harmless, in the case of a fuel tanker, they can lead to catastrophic results.
The Role of the Chain in Grounding Static Electricity
So, why the chain? The metal chain is an essential tool for grounding static electricity. Here’s how it works:
- Conductive Pathway: The chain, made of metal, is highly conductive, meaning it can quickly transfer electric charges. As the truck moves, the chain drags along the ground, creating a direct connection between the tanker and the Earth.
- Discharge of Static Charges: As static electricity builds up on the tank, it flows through the metal chain and disperses safely into the ground. This grounding process neutralizes the charges, preventing sparks that could ignite the flammable liquids within the tank.
- Continuous Grounding: Since the chain is constantly in contact with the ground, it provides continuous grounding, which is essential given the consistent motion of the liquid within the tank. This prevents any potential accumulation of static electricity that could lead to dangerous sparks.
In short, the chain acts as a safety feature that continuously releases static electricity from the tanker, ensuring that dangerous sparks don’t ignite the contents.
Static Electricity: A Hidden Danger When Moving Fuel
While it might seem like static electricity is only a problem when a tanker truck is in motion, the risk doesn’t disappear when the truck is stationary. In fact, static charges can accumulate even when the truck is being loaded or unloaded with fuel.
Consider this: as fuel is pumped into or out of the truck, it moves through pipes and hoses, generating friction that can create static electricity. This is why tanker trucks not only rely on the chain but also make use of other grounding systems when stationary. In most cases, specialized grounding devices, such as the RTR – Road Tanker Grounding system, are employed to further neutralize static electricity during the loading and unloading process.
Beyond Chains: The Importance of Grounding Systems in Fuel Transport
While the dragging chain is a simple and effective grounding tool for moving trucks, stationary tanker trucks often require more robust grounding solutions. Systems like the RTR – Road Tanker Grounding (Earthing) system are commonly used to ensure a solid grounding connection while the truck is parked. Here’s how these systems add an extra layer of safety:
- Additional Grounding: When the truck stops to load or unload, it’s typically connected to a grounding terminal at the fueling station. This ensures that any static electricity generated during fuel transfer is immediately grounded, minimizing the risk of sparks.
- Continuous Monitoring: Many of these grounding systems have built-in monitoring to ensure that a proper connection is maintained throughout the loading or unloading process. If the connection is lost or compromised, the system will alert the operator, halting fuel transfer until the grounding issue is resolved.
Together, these grounding measures – both the chain and specialized grounding systems – are designed to reduce the risk of fire and explosion by continuously dispersing static electricity.
The Science Behind Static Electricity and How It Can Lead to Explosions
Static electricity is a common phenomenon in our everyday lives, but it becomes dangerous when it’s coupled with flammable materials. When an electric charge builds up on the surface of a material (like the metal of a tanker truck), it remains there until it’s released. In cases where the charge becomes strong enough, it will discharge in the form of a spark.
If this spark occurs near a source of fuel vapor, it can ignite the vapor, causing an explosion. This is precisely why tanker trucks need reliable grounding measures in place. By continuously discharging static electricity, these safety features help prevent the formation of sparks and reduce the risk of catastrophic accidents.
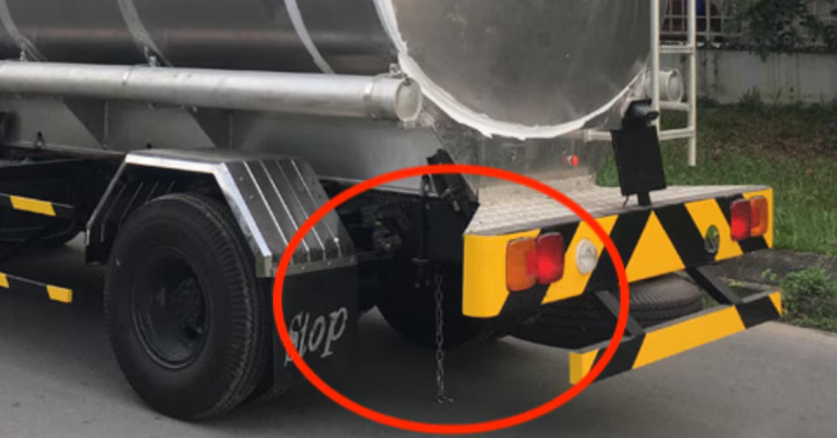

Other Situations Where Grounding is Essential
Tanker trucks aren’t the only situations where grounding static electricity is important. Similar precautions are taken in various industries that deal with flammable or explosive materials, such as chemical plants and gas stations. In these environments, grounding systems are commonly used to prevent static buildup and ensure a safe working environment.
For instance:
- Gas Stations: At the pump, grounding measures ensure that static electricity generated from the flow of fuel is safely dispersed. Some pumps even require the nozzle to touch the car’s gas tank before fueling can begin, grounding the vehicle and minimizing the chance of static sparks.
- Airplanes: After landing, airplanes are often grounded before fuel is transferred to avoid any static buildup that could ignite fuel vapors.
Conclusion: The Small Chain with a Big Role in Safety
The extra chain hanging at the back of a tanker truck may seem insignificant, but it’s a small, simple feature that plays a big role in ensuring safety. By providing continuous grounding, the chain prevents static electricity from building up and causing sparks that could lead to fires or explosions. Along with other grounding systems, it serves as a reminder that when it comes to transporting flammable liquids, every precaution counts.
Next time you see a tanker truck on the road, you’ll know that the chain dragging behind is more than just a piece of metal – it’s a crucial safety tool designed to protect us all.



